Computed Tomography (CT) data-analysis software analyses additively-manufactured molds and their prototypes for deviations and defects to improve quality and speed design iteration
August 13, 2019 — Charlotte, NORTH CAROLINA — Volume Graphics, the leading provider of industrial CT software according to management consultants Frost & Sullivan, has announced its involvement with the Kunststoff-Institut in a second joint project on “Rapid Tooling” with companies from a wide range of industries. As a project partner, Volume Graphics brings expertise in quality assurance and process optimization to the team via its advanced industrial computed tomography (CT) data-analysis software.
“Working on this project with Kunststoff-Institut and partners is very important to us,” explains Christof Reinhart, CEO of Volume Graphics, “because we are convinced that industrial computed tomography can advance the future of rapid tooling. We have been following the topic of additive manufacturing in general and rapid tooling in particular for some time now and are working on solutions to increase prototype volumes, speed of design and overall part-and-process quality.”
Additive manufacturing’s growing role in rapid tooling
In tool and mold making, additive manufacturing (AM, aka 3D printing) is playing an increasingly important role in the quality and economics of high-efficiency metal production tooling with conformal cooling channels, and rapid prototyping of sample parts and plastic mold inserts. Mold inserts are a focus of the Consortium’s second project because of their critical importance in strengthening parts and/or encapsulating fabricated components.
The development phase of creating injection molded parts and inserts often requires the production of small-quantity prototypes. Two common approaches are, first, the modeling of sample “presentation” components using a low-end rapid process and, second, the more complicated method of using an aluminum molding tool, where the final part in the prototype production process is completed with an injection molding machine.
However, a new “rapid” method offers improved time and cost savings over aluminum: plastic molds —
produced through industrial AM—that are then used for prototyping traditional plastic components with inserts. While the sample output is lower in plastic molds than in aluminum, plastic is proving more than sufficient for prototypes and is less expensive than metal.
CT data-analysis software: a deeper dive into inspection and correction
Industrial CT has been an indispensable technology in tool and mold inspection for years, allowing non-destructive testing of manufactured components. Volume Graphics’ software provides a much deeper look into CT results, revealing flaws that may be invisible to the naked eye, comparing as-manufactured parts to their original designs and simulating the performance of part geometries to guide design and/or manufacturing corrections. Comparisons between CT and CAD datasets reduce molding-tool corrections for defects and warpage to a minimum.
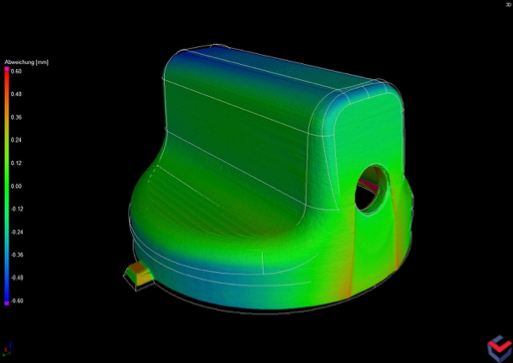
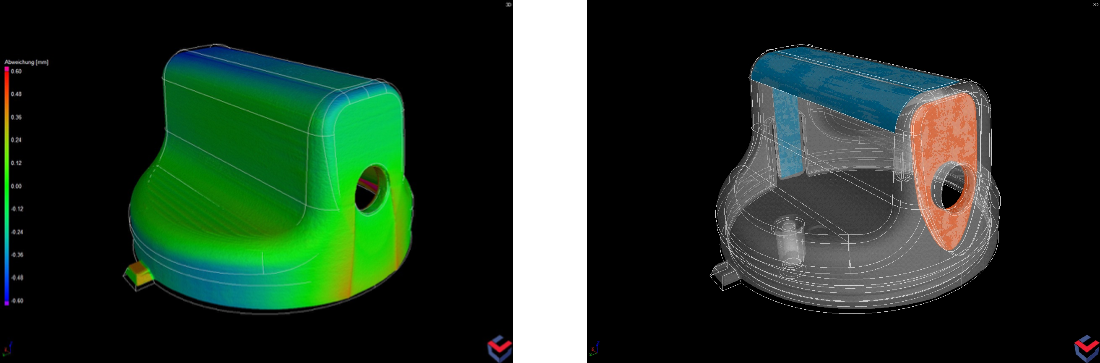
Comparison of manufactured mold-insert part with nominal geometry in Volume Graphics’ software.
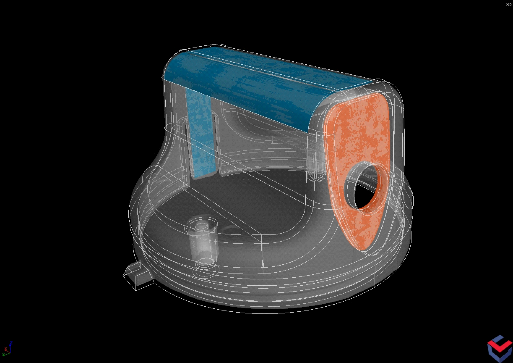
Manufacturing geometry correction module from Volume Graphics adjusts design of mold-insert surfaces to compensate for warpage in the additively manufactured mold prototype.
The latest versions of Volume Graphics’ CT analysis software packages VGSTUDIO MAX and VGMETROLOGY provide a Manufacturing Geometry Correction module, which has been specifically developed by Volume Graphics for tool and mold making and additive manufacturing. Part shrinkage, distortion or other dimensional deviations detected in the CT data set can be transferred to the CAD model of the tool in order to analyze and redesign the relevant contour so that it 3D-prints correctly.
“With our Manufacturing Geometry Correction module we have laid the foundation for many new applications in tool and mold making that can take advantage of improving speed and quality developments in additive manufacturing,” says Reinhart. “This data can be of great use to tool designers, to improve both the tool design itself and the 3D-printing strategy used to manufacture it.”
About The Kunststoff-Institut
The Kunststoff-Institut was founded in 1988 in Germany as the first institute associated with a university of applied sciences. Currently there are more than 340 member companies. Those involved in the molding project described here include DMG Digital Enterprises, ebm-papst Mulfingen GmbH & Co. KG, Faurecia Autositze GmbH, Fritz Schäfer GmbH, Günther Spelsberg, Habasit AG, Montblanc-Simplo GmbH, Parker Hannifin Technology, Quarzwerke GmbH, rpm, SimpaTec GmbH, Sonova AG, Volume Graphics GmbH, V-ZUG AG.
About Volume Graphics
Volume Graphics GmbH has been developing software for non-destructive testing based on industrial computed tomography (CT) for over 20 years. With a market share of around 80%, Volume Graphics occupies a leading position in the industrial CT software industry, as confirmed by the global management consultancy Frost & Sullivan with the “2018 Global Industrial CT Software Market Leadership Award”. Customers around the world, e.g., from the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries, use Volume Graphics software for quality assurance in product development and production. In addition to its headquarters in Heidelberg, the company has branches in the USA, Japan, Singapore, and China. Further information can be found at: www.volumegraphics.com
U.S. contact:
Hannah Weinreich
Volume Graphics Inc.
weinreich@volumegraphics.com
